
As part of the IoT Hacks series, we have already covered Bluetooth technology – new features released for Bluetooth versions 5.0 to 5.2. This time we will tell you about LoRaWAN protocol. You will get to know what it is, how it is used in general, what kind of network infrastructure it requires, and how it can be used on a day-to-day basis. We are still continuing the series, where we share useful insights and tips on how to reduce power consumption when you are creating IoT solutions.
LoRa (an acronym for long range) is a modulation method based on CSS[1] (chirp spread spectrum), which provides a long range with low power consumption at the expense of bandwidth.
LoRaWAN (LoRa Wide Area Network) is a communication protocol[2] using LoRa modulation intended for use in Internet of Things devices. It is a star topology protocol in which end devices connect to an application server through a series of gateways.
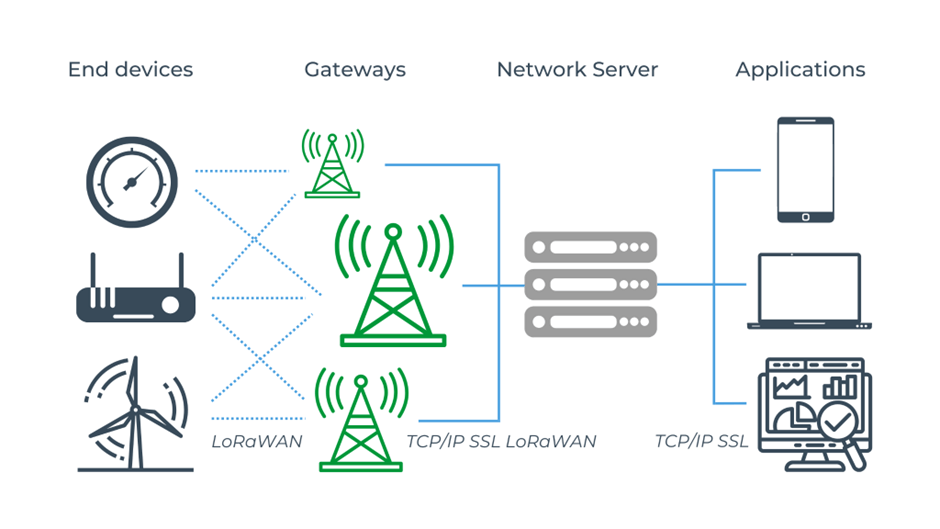
The utilization of LoRa modulation in the physical layer means that, in order to achieve the same range, the transmitter power can be lower than in competing protocols, thus ensuring a longer battery life. A feature worth noting in the LoRaWAN communication protocol is the ADR[3]mechanism (Adaptive Data Rate). It allows for the adaptive adjustment of transmission speed and transmitter power to optimize bandwidth and energy consumption.
The LoRaWAN protocol is open and uses unlicensed frequencies of the ISM band[4], which makes its implementation and use free of charge. Sounds good, right?
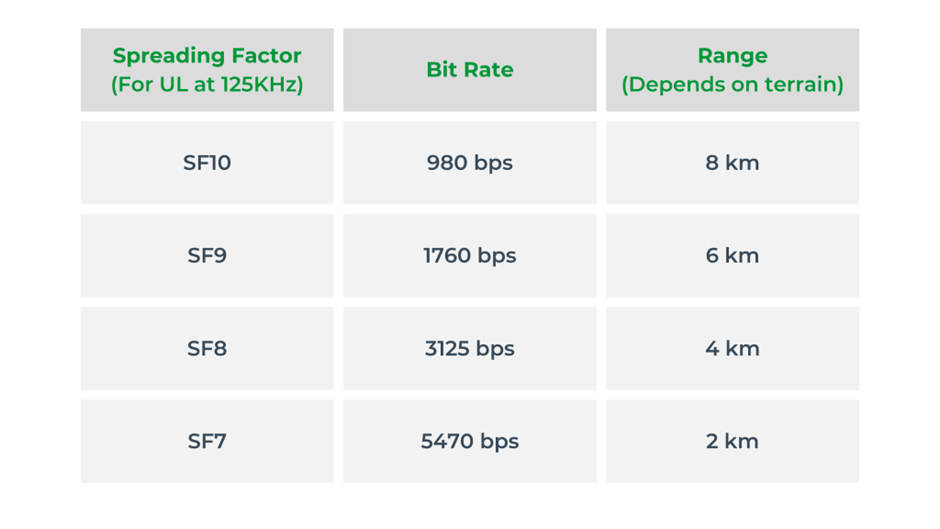
Keep in mind though, that range, as outlined above, is strongly bandwidth-dependent in the LoRaWAN protocol. Here are the results that can be achieved. See the table below:
Current consumption, and thus battery life, ultimately depends on the intended design of the device, the peripherals connected, and the frequency of message exchange. It is therefore quite hard to give reliable information in this respect without being aware of these details. Nonetheless, when browsing through the devices available on the market, a majority of them show the working time on a single set of batteries not in days or months, but in years. With such low power consumption, “energy harvesting” makes a sound addition to the IoT device, as we have already explained here in the article: IoT Hacks #1: Energy harvesting for low-power embedded systems.
If you are looking to develop a new IoT product using the LoRaWAN protocol (LoRa Wide Area Network), you can base it on a microcontroller with an embedded LoRaWAN network stack or use a ready-made, certified module for it. These approaches vary by complexity and technical capability, but what is crucial here to consider is when you plan to launch the product. Off-the-shelf solutions may speed up the release, but they may not meet your expectations in terms of functionality. Before reaching a decision on technology, we strongly recommend that you carry out an in-depth case study. If you’re stuck on this step, we’re happy to help. We’ve been delivering embedded systems and IoT projects for years, so we really know how to get the digital product development process sorted out.
But what if your product is already on sale and you now want to enhance it with network connectivity without making any massive changes to its architecture? Great news! Nothing stands in your way! The market is full of routers with a complete stack, both in the form of integrated circuits, as well as certified modules that can be attached to your device. Again, bear in mind, a thorough analysis of the solution and the expected new functionalities is not to be missed.
All IoT products utilizing wireless communication (regardless of the type) still need the right infrastructure. At home or in a company, WiFi access points are put in place. When creating a building automation system, Bluetooth or Wi-SUN gateways are often used.
What happens in the case of urban agglomerations? Until now, the only commonly available medium has been the mobile network, which is, at the same time, expensive to implement and operate, as well as very energy-consuming. Plus it is not conducive to the efficient performance of Internet of Things devices. The aforementioned Wi-SUN network also manifests features suitable for use in such applications. But the problem of infrastructure availability still stands. You can read more about this topic in one of our previous articles from the IoT Hacks series – #3 Wi-SUN in IoT systems.
So, where does this leave us? Well, the concept of LoRaWAN system networks built by the community interested in this solution, such as Helium or TheThingsNetwork, comes to the rescue.
At the date of this article’s publication, the Helium network is well covering the area of the majority of large cities in Poland [5]. The charging method using this network is quite similar to that of mobile networks (you pay for the transfer used). What is more to the point, it is a LoRaWAN system network, hence it ensures low power consumption. And what needs to be highlighted – there’s no need to worry about infrastructure, as it is already there!
Should you not want to be reliant on the existing infrastructure (or want your network to run indoors), then there is nothing stopping you from taking a standard approach and building a network of gateways. However, it is worth pointing out that LoRaWAN protocol is the only one that brings such possibilities in the context of IoT devices.
The world is in flux. All sorts of services get more and more interactive and the technical possibilities are surging, too. Communication between people and objects (as odd as it may sound) has never been so ubiquitous and straightforward. After all, is there anyone out there at this point surprised by a notification on their mobile phone informing them that their laundry is done? New concepts such as Helium are emerging, paving the way for many ideas and products that were previously shut off.
The examples of LoRaWAN applications are countless, starting from citywide applications (intelligent lighting, air quality verification, or city parking management with interactive information for drivers), through office and industrial applications (monitoring of production, desk occupancy, or lighting control in office buildings and factories), to home appliances (roller blinds, heating control or monitoring of plant watering levels).
It is fair to say that the LoRaWAN protocol is “tailor-made” for IoT products. It is fast enough, energy-efficient with a long-range and implementation-friendly, as well as it provides some unique capabilities in terms of infrastructure availability. This can also be demonstrated by the sheer number of products on the market that have already leveraged LoRaWAN.
